
By Dr. A. Sajidas, Managing Director, BIOTECH INDIA Renewable Energy. International Consultant - Biogas, Organic Waste Management & Sustainable Development
The ozone layer, a delicate shield of gas in the stratosphere, is vital for life on Earth. It absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, preventing skin cancer, cataracts, reduced crop yields, and damage to ecosystems. Over the years, however, the ozone layer has faced severe threats from human activities. Chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other ozone-depleting substances (ODS) have caused thinning and the infamous "ozone hole" In addition, emissions of greenhouse gases like methane contribute indirectly to ozone depletion by intensifying global warming and altering atmospheric chemistry.
Among the many strategies for environmental protection, biogas technology has emerged as a powerful solution. Biogas plants not only provide renewable energy but also reduce harmful emissions and mitigate the conditions that accelerate ozone depletion. This blog explores in detail how biogas plants contribute to the protection of the ozone layer and create a pathway toward a sustainable future.
Biogas is a clean, renewable fuel produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter such as food waste, animal manure, crop residues, and sewage. In a biogas plant, microorganisms break down these wastes in an oxygen-free environment, releasing a mixture of gases mainly composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
The key outputs of a biogas plant include:
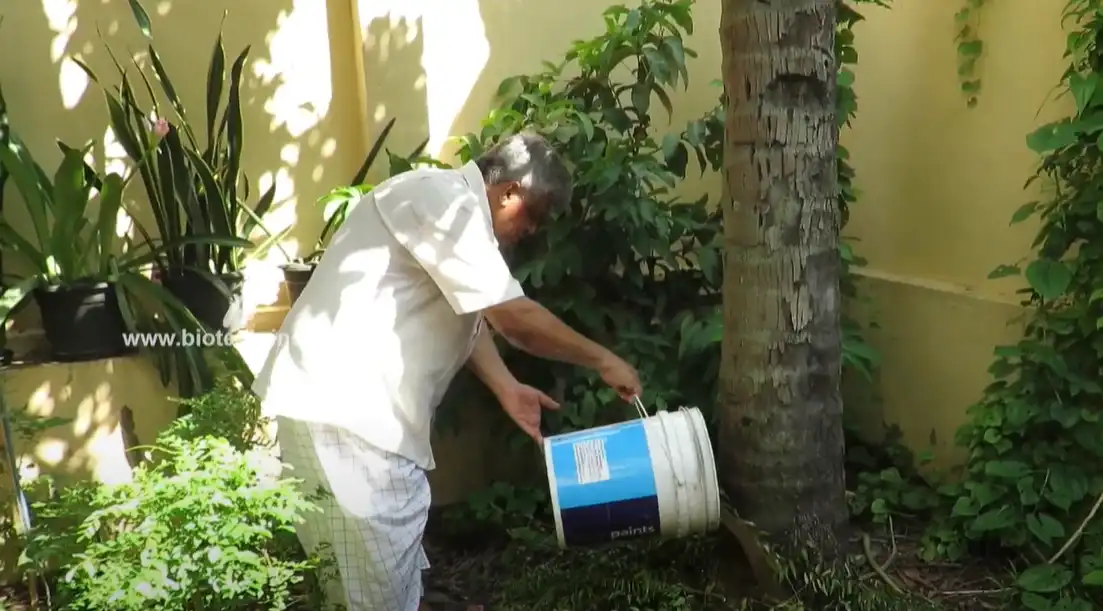

1. Biogas: A clean fuel that can be used for cooking, heating, electricity generation, or even as vehicle fuel after purification.
2. Digestate: A nutrient-rich organic slurry that serves as an excellent natural fertilizer, reducing the need for chemical alternatives.
This simple yet highly effective technology not only produces renewable energy but also addresses multiple environmental challenges simultaneously.
The depletion of the ozone layer has been primarily caused by the release of man-made chemicals such as CFCs, halons, and carbon tetrachloride. These chemicals, once widely used in refrigeration, aerosols, and solvents, rise into the stratosphere where they release chlorine and bromine atoms that destroy ozone molecules.
In addition to these direct causes, greenhouse gases such as methane indirectly contribute to ozone layer damage. Methane, when released into the atmosphere, reacts with hydroxyl radicals and produces water vapor in the stratosphere. This added water vapor enhances chemical reactions that deplete ozone. Thus, controlling methane emissions is an important step in ozone protection.
1. Methane Capture and Utilization
Organic waste left in open dumps, landfills, or untreated sewage systems naturally emits methane as it decomposes. Methane is over 25 times more potent than CO2 in causing global warming and contributes indirectly to ozone depletion.
Biogas plants capture this methane and convert it into usable energy. Instead of escaping into the atmosphere, methane becomes a resource. This single function of biogas technology significantly reduces harmful emissions and eases pressure on the ozone layer.
2. Reduction of Fossil Fuel Dependence
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are the backbone of conventional energy systems, but they release vast quantities of greenhouse gases and pollutants. Many of these by-products alter atmospheric chemistry, affecting both climate and ozone health.
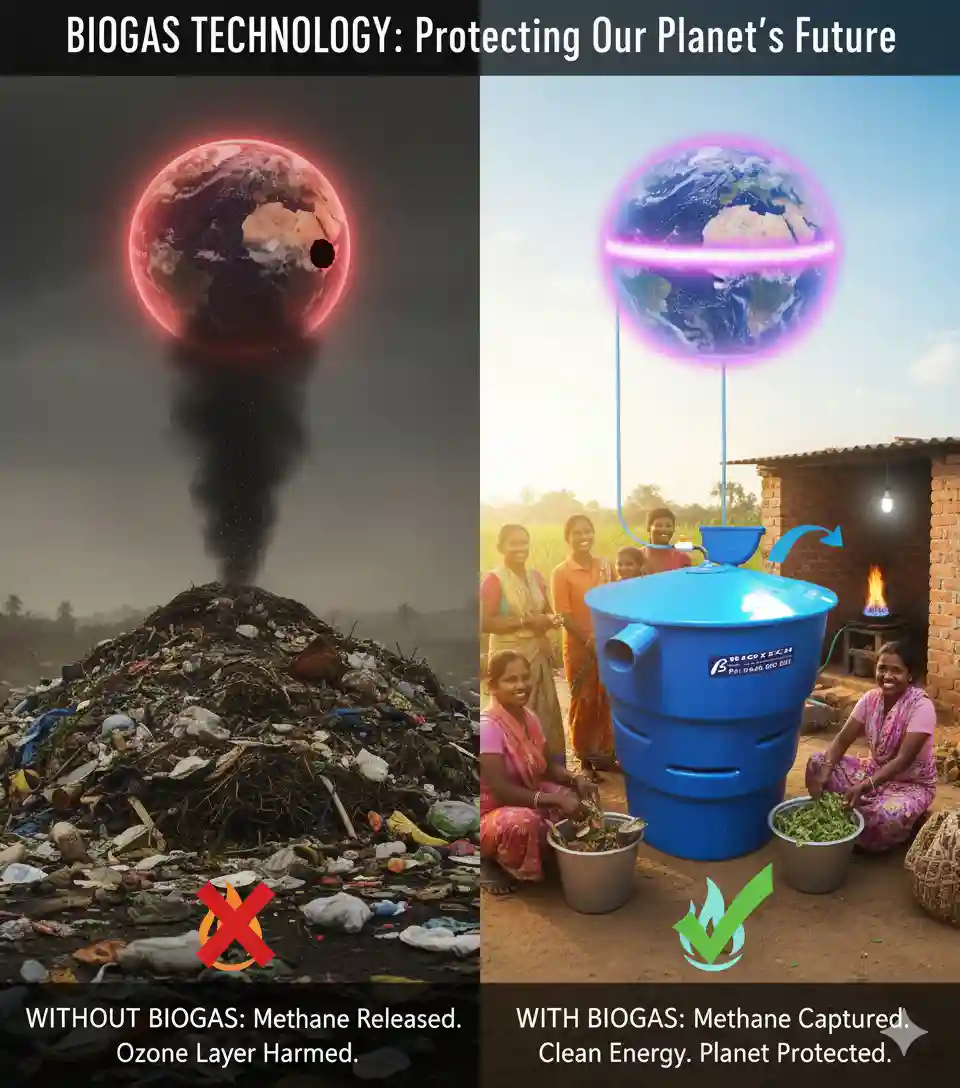

By providing renewable energy, biogas plants reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Every unit of energy generated from biogas replaces an equivalent unit that would have come from coal or petroleum, thereby reducing harmful emissions and helping preserve the ozone layer.
3. Prevention of Open Burning of Waste
In many parts of the world, agricultural residues, food waste, and animal manure are often burned in the open. This practice releases carbon monoxide, nitrous oxides, and volatile organic compounds, some of which contribute to ozone layer depletion and local air pollution.
Biogas plants offer a sustainable alternative by converting these wastes into fuel and fertilizer. Preventing open burning not only reduces air pollution but also supports the global effort to protect the ozone shield.
4. Production of Organic Fertilizer
The digestate from biogas plants is a valuable organic fertilizer. It reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which often emit nitrous oxide (N2O) during their production and use. Nitrous oxide is a greenhouse gas that is nearly 300 times more potent than CO2 and is also recognized as an ozone-depleting substance.
By replacing chemical fertilizers with digestate, biogas plants minimize nitrous oxide emissions, further contributing to the preservation of the ozone layer.
5. Integration with Climate Protection Goals
The success of the Montreal Protocol in reducing ODS has shown that global cooperation can heal the ozone layer. Today, climate change is closely linked to ozone protection, as both are influenced by the same set of gases. Biogas plants address climate change by reducing greenhouse gases and simultaneously help ozone recovery.
Thus, biogas technology serves as a bridge between renewable energy development, waste management, and ozone layer protection.


India
India has been a pioneer in household and institutional biogas programs. Millions of family-size plants have been installed, particularly in rural areas. By managing animal manure and kitchen waste, these plants prevent methane release and provide clean cooking energy, reducing reliance on firewood and fossil fuels. This indirectly contributes to ozone layer protection by cutting emissions.
BIOTECH India has played a pioneering role in the promotion and implementation of biogas projects across India. As a leading renewable energy organization, it has developed and popularized innovative, user-friendly biogas plant models suitable for households, institutions, and community-level applications. By focusing on decentralized waste management, BIOTECH India converts organic waste into clean energy and organic fertilizer, addressing multiple challenges such as waste disposal, energy scarcity, and environmental pollution.
The organization has successfully installed thousands of biogas plants in urban and rural areas, providing sustainable cooking fuel, electricity, and waste treatment solutions. Its efforts have reduced methane emissions, prevented open dumping and burning of waste, and promoted the use of renewable energy. Through training, awareness programs, and international collaborations, BIOTECH India continues to demonstrate how biogas technology can contribute to climate protection, sustainable development, and improved livelihoods in India.
Germany
Germany has integrated biogas into its renewable energy strategy. Large-scale biogas plants produce electricity and heat, significantly reducing the country's dependence on coal. By doing so, they cut emissions of gases that negatively affect the ozone layer and global climate.
African Nations
In Sub-Saharan Africa, decentralized biogas plants are addressing both energy scarcity and environmental challenges. They reduce open burning of crop residues and dung, a major source of harmful emissions. These projects not only improve local livelihoods but also contribute globally to ozone protection.
While the direct role of biogas plants in protecting the ozone layer is clear, their broader benefits also reinforce their importance:
⇒ Health Protection: Cleaner cooking energy reduces indoor air pollution, protecting women and children from respiratory diseases.
⇒ Sustainable Agriculture: Organic digestate improves soil fertility without harming ecosystems.
⇒ Circular Economy: Biogas plants transform waste into valuable resources, creating a closed-loop system.
⇒ Job Creation: Installation and maintenance of biogas plants create employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
All these benefits collectively support global sustainability and reduce pressures that indirectly affect the ozone layer.
Despite their immense potential, biogas plants face challenges that limit their large-scale adoption:
⇒ High Initial Costs: Many households and institutions cannot afford the upfront investment.
⇒ Lack of Awareness: Communities are often unaware of the multiple environmental benefits of biogas.
⇒ Technical Barriers: Poor design, lack of maintenance, and improper feedstock management can lead to plant failures.
⇒ Policy Support: In many regions, biogas development is not fully integrated into national renewable energy and climate strategies.
To maximize the role of biogas in protecting the ozone layer, the following steps are essential:
1. Government Incentives: Subsidies, tax benefits, and soft loans to encourage adoption.
2. Awareness Campaigns: Linking biogas use with ozone protection in public communication.
3. Research and Innovation: Developing low-cost, user-friendly plant designs.
4. International Cooperation: Sharing best practices across countries, just like the success of the Montreal Protocol.
The protection of the ozone layer is not just about eliminating harmful chemicals like CFCs; it also requires tackling greenhouse gases and waste management challenges that indirectly affect atmospheric balance. Biogas plants stand at the intersection of energy, environment, and sustainability. By capturing methane, reducing fossil fuel use, preventing waste burning, and replacing chemical fertilizers, they make a significant contribution to ozone preservation.
World Ozone Day reminds us of the importance of global cooperation in healing our atmosphere. Just as the Montreal Protocol became a symbol of environmental success, widespread adoption of biogas technology can become a model for integrated climate and ozone protection. Investing in biogas today is investing in a cleaner sky, a safer ozone shield, and a healthier planet for future generations.
Telephone: +91-471-2331909, 2321909, 2332179
E-mail: mailtobiotech@gmail.com


Ernakulam (Cochin)
Telephone: +91-484-4858695
E-mail: mailtobiotech@gmail.com


Kozhikode (Calicut)
Mob : +91-9446-000-962
E-mail: mailtobiotech@gmail.com


Telangana
Telephone: +91 40 29330078 , +919446000968
E-mail: gtp.nird@gmail.com

